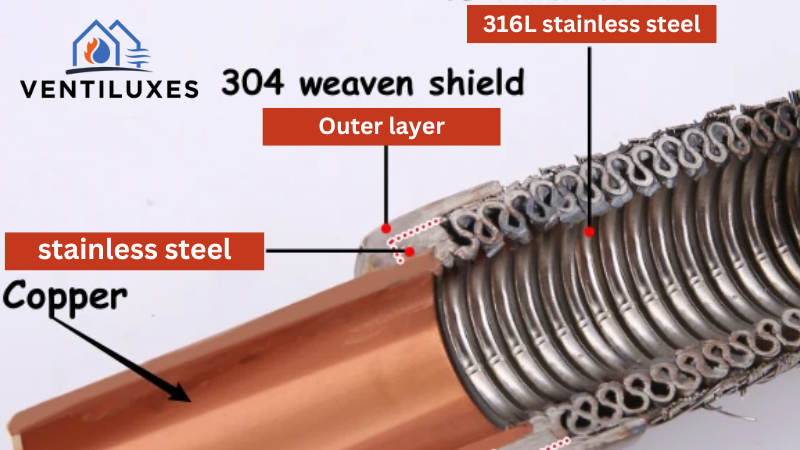
An AC is a combination of multiple interconnected wires and lines. One of those is the Suction Line. A copper pipe pulls low-pressure cold refrigerant from the evaporator inside and throws it at the outside compressor. The metal tube is made of durable copper and steel.
It is also insulated later on to protect against the ambient heat. Refrigerant lines also do these jobs:
- Transports Refrigerant: The suction line carries low-pressure — cold refrigerant from the indoor evaporator coil to the outdoor compressor unit.
- Prevents Efficiency Loss: It minimizes the absorption of ambient heat, ensuring the refrigerant remains cold and thus maintains system efficiency.
- Supports Cooling Cycle: This line is essential for completing the refrigeration cycle.
- Reduces Energy Costs: Effective insulation and maintenance of the suction line help reduce energy consumption and lower electricity bills.
- Maintains System Health: Proper function and insulation of the suction line prevent issues like refrigerant leaks.
How Does the Suction Line Work?
If you want to understand how suction lines work, it’s not rocket science. The suction line in an HVAC system transports warm refrigerant from the house to the outdoor unit. It is covered in a metal or plastic pipe to prevent heat loss and moisture buildup and to help prevent wall damage.
As warm air flows through the indoor unit’s cooling coils, it cools while dust and debris are filtered out, improving indoor air quality. Thus, keeping suction lines clear is a must to maintain efficient airflow and prevent AC freezing issues—the suction and liquid lines cycle refrigerants to produce hot or cool air.
Where is the Suction Line Located?
The suction line of an AC is on the side of the outdoor unit or compressor. It comes from the indoor unit, along with the roof and behind insulation. If you can’t find it, check the unit’s backside—there should be a small hole where the suction line enters.
5 Signs & Common Issues with AC Suction Lines
The performance of an AC heavily relies on the condition of its suction line. However, several issues can impair its efficiency, such as:
- Overheating: If the suction line is clogged, improperly sized, bent, or kinked, it restricts refrigerant flow.
- Inadequate Cooling: A compromised line might not deliver enough refrigerant to the compressor, leading to poor cooling performance.
- Frost or Ice Formation: Any blockages or size mismatches can cause refrigerants to accumulate and freeze. You’ll see frost or ice on the outer layer of the line itself.
- Low Amperage: Insufficient refrigerant flow can also lead to lower-than-normal amperage in the compressor.
- System Malfunctions: In severe cases, these issues might cause the entire AC system to stop working. Thus, immediate repairs are required to prevent extensive damage and restore proper function.
Ideal Suction Line Size – What to Consider?
A small diameter might suffice for smaller setups, but larger homes might require a big hole line to handle the flow. You can check the manual guide to figure out the most suitable diameter.
Whole Vs. Joined Suction Line
Sometimes, homeowners must choose between a whole suction line length and a jointed length.
But why?
The situation changes for installations that require long lengths to connect the indoor with the outdoor.
Let’s find out what will be the best option in this case:
| Feature | Whole Suction Line | Jointed Suction Line |
|---|---|---|
| Installation Complexity | Simple, straightforward installation | More complex due to multiple connections |
| Cost | Higher initial cost | Lower initial cost |
| Maintenance | Lower maintenance needs | Potentially higher maintenance due to joints |
| Durability | Generally more durable, less prone to leaks | Potential for leaks at joints |
| Flexibility | Less flexible in routing | More flexible in routing |
| Repair | May require replacing the entire line | Easier to replace sections |
| Performance | Consistent performance, less airflow disruption | Possible airflow disruption at joints |
As professional technicians, we prefer to go the whole length most of the time. In contrast, if the house structure is more complex, then we do either install the connected suctions as well.
FAQs
What is the expected lifespan of AC suction lines?
On average, AC suction lines last 10 to 25 years, but this can vary depending on the material quality and maintenance frequency. Consult an HVAC professional when considering replacement.
How does a Suction Line Filter dryer function in an HVAC system?
A Suction Line Filter Dryer removes moisture and impurities from the refrigerant. It protects the compressor and extends system health.


Leave a Reply